Filters LAS/LAZ
When launching the filters, we are greeted with a startup window.
Statistical Outlier Removal (SOR) is a method that first calculates the average distance between each point and its neighbors. It then removes points that are more than the average distance plus a few standard deviations. The minimum number of neighboring points is 6 and the standard deviation is 1.
Noise removal is a method that is similar to statistical outlier removal (SOR), but it considers the distance to the main surface rather than neighboring points. It locally fits a plane around each cloud point and removes a point if it is too far from that plane. This filter can be thought of as a low-point filter.
Surface reconstruction is a technique that is used to create complete surface models from heterogeneous data. Sometimes small errors in distance measurements can lead to difficulties in removing anomalies by statistical analysis. In such cases, surface reconstruction uses a resampling algorithm that attempts to reconstruct missing parts of the surface by polynomial interpolation between surrounding data points. This corrects small errors and smooths out artifacts such as "double walls" that occur when multiple scans are recorded simultaneously.
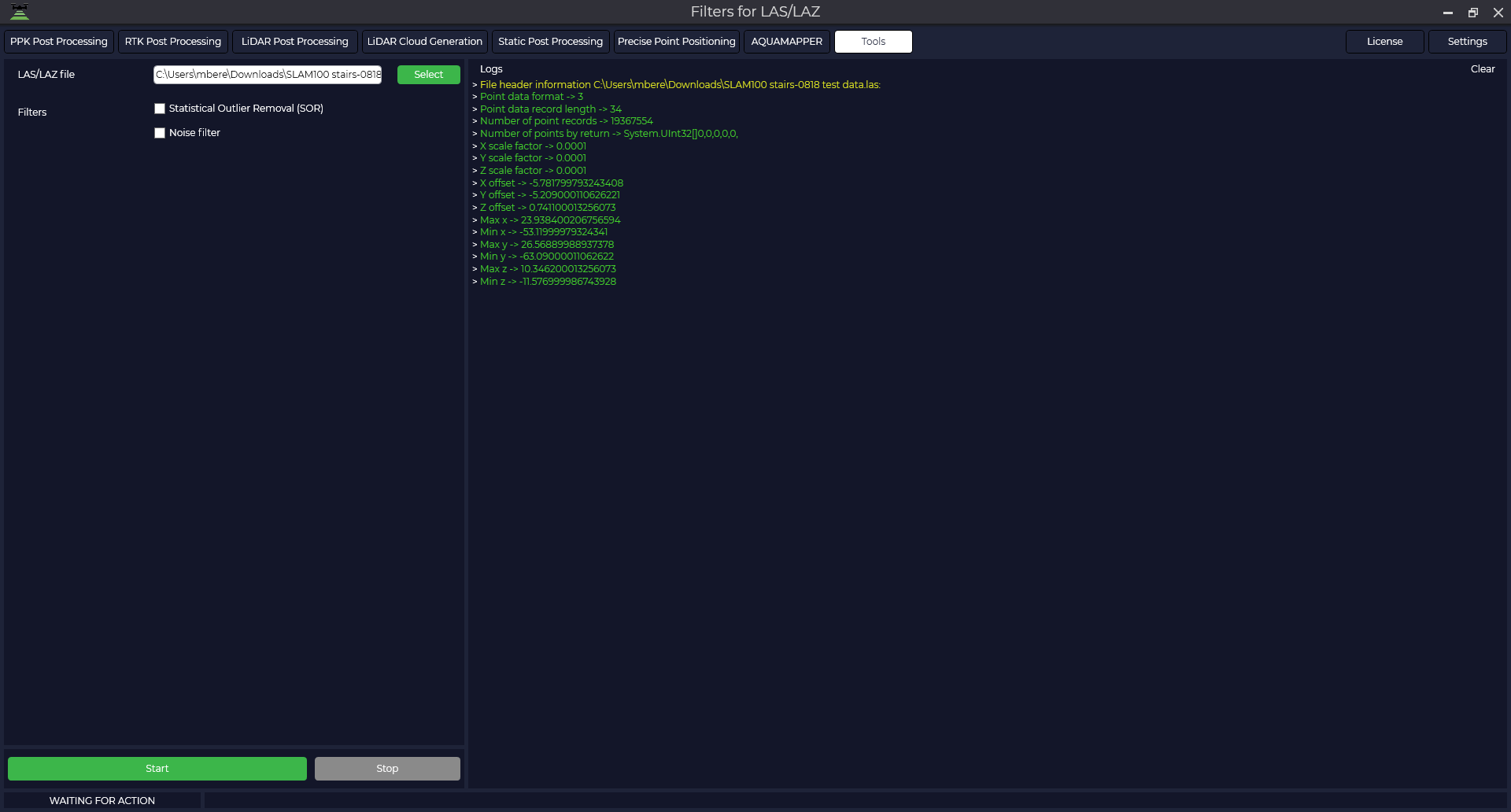
If you select a file in LAS or LAZ format, the login window will display the information contained in the file: number of points, X, Y, Z offsets, etc.
To process, check the required filters and press the "Start" button. If several filters are selected, they are applied sequentially. All results are saved to the folder with the source file.

No Comments